Abstract
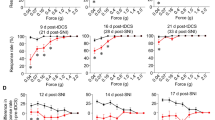
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) induces cortical excitability changes in animals and humans that can last beyond the duration of stimulation. Preliminary evidence suggests that tDCS may have an analgesic effect; however, the timing of these effects, especially when associated with consecutive sessions of stimulation in a controlled animal experiment setting, has yet to be fully explored. To evaluate the effects of tDCS in inflammatory chronic pain origin immediately and 24 h after the last treatment session, complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA) was injected (100 μl) in the right footpad to induce inflammation. On the 15th day after CFA injection, rats were divided into two groups: tDCS (n = 9) and sham (n = 9). The tDCS was applied for 8 days. The hot plate and Von Frey tests were applied immediately and 24 h after the last tDCS session. Eight 20-min sessions of 500 μA anodal tDCS resulted in antinociceptive effects as assessed by the hot plate test immediately (P = 0.04) and 24 h after the last tDCS session (P = 0.006), for the active tDCS group only. There was increased withdrawal latency in the Von Frey test at 24 h after the last session (P = 0.01). Our findings confirm the hypothesis that tDCS induces significant, long-lasting, neuroplastic effects and expands these findings to a chronic pain model of peripheral inflammation, thus supporting the exploration of this technique in conditions associated with chronic pain and peripheral inflammation, such as osteoarthritis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antal P, Paulus W (2011) A case of refractory orofacial pain treated by transcranial direct current stimulation applied over hand motor area in combination with NDA agonist drug intake. Brain Stimul 117:121–124
Antal A, Nitsche MA, Paulus W (2006) Transcranial direct current stimulation and the visual cortex. Brain Res Bull 459:463–468
Apkarian V, Baliki MN, Geha PY (2009) Towards a theory of chronic pain. Prog Neurobiol 87:81–97
Ardolino G, Bossi B, Barbieri S, Priori A (2005) Non-synaptic mechanisms underlie the after-effects of cathodal transcutaneous direct current stimulation of the human brain. J Physiol 568:653–663
Bernardi A, Zilberstein ACCV, Jäger E, Campos MM, Morrone FB, Calixto JB, Pohlmann AR, Guterres SS, Battastini AMO (2009) Effects of indomethacin-loaded nanocapsules in experimental models of inflammation in rats. Br J Pharmacol 158:1104–1111
Bolcskei K, Helyes Z, Szabo A, Sandor K, Elekes K, Nemeth J, Almasi R, Pinter E, Petho G, Szolcsanyi J (2005) Investigation of the role of TRPV1 receptors in acute and chronic nociceptive processes using gene-deficient mice. Pain 117:368–376
Borckardt JJ, Bikson M, Frohman H, Reeves ST, Datta A, Bansal V, Madan A, Barth K, George MS (2011a) A pilot study of the tolerability and effects of high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation (HD-tDCS) on pain perception. J Pain 11:665–671
Borckardt JJ, Romagnuolo J, Reeves ST, Madan A, Frohman H, Beam W, George MS (2011b) Feasibility, safety, and effectiveness of transcranial direct current stimulation for decreasing post-ERCP pain: a randomized, sham-controlled, pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc 73:1158–1164
Brown JA, Barbaro NM (2003) Motor cortex stimulation for central and neuropathic pain: current status. Pain 104:431–435
Bruguerolle B, Labrecque G (2007) Rhythmic pattern in pain and their chronotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:883–895
Brunoni AR, Nitsche MA, Bolognini N, Bikson M, Wagner T, Merabet L, Edwards DJ, Valero-Cabre A, Rotenberg A, Pascual-Leone A, Ferrucci R, Priori A, Boggio PS, Fregni F (2011) Clinical research with transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS): Challenges and future directions. Brain Stimul (in press)
Caggiula AR, Epstein LH, Perkins KA, Saylor S (1995) Different methods of assessing nicotine-induced antinociception may engage different neuronal mechanisms. Psychopharmacology 122:301–306
Carroll D, Joint C, Maartens N, Shlugman D, Stein J, Aziz TZ (2000) Motor cortex stimulation for chronic neuropathic pain: a preliminary study of 10 cases. Pain 84:431–437
Datta A, Bansal V, Diaz J, Patel J, Reato D, Bikson M (2009) Gyri -precise head model of transcranial DC stimulation: improved spatial focality using a ring electrode versus conventional rectangular pad. Brain Stimul 4:201–207
De Santi L, Cantalupo L, Tassi M, Raspadori D, Cioni C, Annunziata P (2009) Higher expression of BDNF receptor gp145trkB is associated with lower apoptosis intensity in T cell lines in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 277:65–70
Derecki NC, Cardani AN, Yang CH, Quinnies KM, Crihfield A, Lynch KR, Kipnis J (2010) Regulation of learning and memory by meningeal immunity: a key role for IL-4. J Exp Med 207:1067–1080
Dockery CA, Liebetanz D, Birbaumer N, Malinowska M, Wesierska MJ (2011) Cumulative benefits of frontal transcranial direct current stimulation on visuospatial working memory training and skill learning in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 96:452–460
Drouot X, Nguyen JP, Peschanski M, Lefaucheur JP (2002) The antalgic efficacy of chronic motor cortex stimulation is related to sensory changes in the painful zone. Brain 125:1660–1664
Fertonani A, Rosini S, Cotelli M, Rossini PM, Miniussi C (2010) Naming facilitation induced by transcranial direct current stimulation. Behav Brain Res 208:311–318
Fregni F, Boggio PS, Lima MC et al (2006a) A sham-controlled, phase II trial of transcranial direct current stimulation for the treatment of central pain in traumatical spinal cord injury. Pain 122:197–209
Fregni F, Gimenes R, Valle AC, Ferreira MJL, Rocha RR, Natalle L, Bravo R, Rigonatti SP, Freedman SD (2006b) A randomized, sham-controlled, proof of principle study of transcranial direct current stimulation for the treatment of pain in fibromyalgia. Arthr Rheum 54:3988–3998
Fregni F, Feedman S, Pascual-Leone A (2007) Recent advances in the treatment of chronic pain with non-invasive rain stimulation techniques. Lancet Neurol 6188:6191
Fritsch B, Reis J, Martinowich K, Schambra HM, Ji Y, Cohen LG, Lu B (2010) Direct current stimulation promotes BDNF-dependent synaptic plasticity: potential implications for motor learning. Neuron 66:198–204
Gandiga PC, Hummel FC, Cohen LG (2006) Transcranial DC stimulation (tDCS): a tool for the double-blind sham-controlled clinical studies in brain stimulation. Neurophysiology 117:845–850
Gomez RS, Guatimosim C (2003) Mechanism of action of volatile anesthetics: involvement of intracellular calcium signaling. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 2:123–129
Head BP, Patel HH, Niesman IR, Drummond JC, Roth DM, Patel PM (2009) Inhibition of p75 neurotrophin receptor attenuates isoflurane-mediated neuronal apoptosis in the neonatal central nervous system. Anesthesiology 110:813–825
Helyes Z, Szabo A, Nemeth J, Jakab B, Pinter E, Banvolgyi A, Kereskai L, Keri G, Szolcsanyi J (2004) Antiinflammatory and analgesic effects of somatostatin released from capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve terminals in a Freund’s adjuvant-induced chronic arthritis model in the rat. Arthr Rheum 50:1677–1685
Jensen MP, Grierson C, Tracy-Smith V, Bacigalupi SC, Othmer S (2007) Neurofeedback treatment for pain associated with complex regional pain syndrome type I: a case series. J Neurother 11:45–53
Ji RR, Kohno T, Moore KA (2003) Central sensitization and LTP: do pain and memory share similar mechanisms? Trends Neurosci 26:696–705
Kubo K, Nishikawa Koichi, Ishizeki J, Hardy-Yamada M, Yanagawa Y, Saito S (2009) Thermal hyperalgesia via supraspinal mechanisms in mice lacking glutamate decarboxylase 65. JPET 331:162–169
Lefaucheur JP (2006) The use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in chronic neuropathic pain. Neurophysiol Clin 117:124–136
Leigh A, Lamont DVM, William J, Tranquilli DVM, Tranquilli DVM, Tranquilli DVM, Kurt A, Grimm DVM (2000) Physiology of pain. Manag Pain 30:703–728
Li Y, Tian X, Qian L, Yu X, Jiang W (2011) Anodal transcranial direct current stimulation relieves the unilateral bias of a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2011:765–768
Lichtenberger LM, Romero JJ, Dial EJ, Moore JE (2008) Naproxen-PC: a GI safe and highly effective anti-inflammatory. Inflammopharmacology 1:5–17
Liebetanz D, Nitsche MA, Tergau F, Paulus W (2002) Pharmacological approach to the mechanisms of transcranial DC-stimulation-induced after-effects of human motor cortex excitability. Brain 125:2238–2247
Liebetanz D, Klinker F, Hering D, Koch R, Nitsche MA, Potschka H, Löscher W, Paulus W, Tergau (2006) Anticonvulsant effects of transcranial direct-current stimulation (tDCS) in the rat cortical ramp model of focal epilepsy. Epilepsia 47:1216–1224
Liebetanz D, Koch R, Mayenfels S, König F, Paulus W, Nitsche MA (2009) Safety limits of cathodal transcranial direct current stimulation in rats. Clin Neurophysiol 120:1161–1167
Lima MC, Fregni F (2008) Motor cortex stimulation for chronic pain: systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Neurology 2329:37–70
Linton SJ (1987) Chronic pain: the case for prevention. Behav Res Ther 313:317–325
Lorton D, Lubahn C, Engan C, Schaller J, Felten DL, Bellinger DL (2000) Local application of capsaicin into the draining lymph nodes attenuates expression of adjuvant-induced arthritis. NeuroImmuno Modul 3:115–125
Lu LX, Yon JH, Carter LB, Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2006) General anesthesia activates BDNF-dependent neuroapoptosis in the developing rat brain. Apoptosis 11:1603–1615
Ma QP, Woolf CJ (1996) Progressive tactile hypersensitivity: an inflammation-induced incremental increase in the excitability of the spinal cord. Pain 67:97–106
Maarawi J, Peyron R, Mertens P et al (2007) Motor cortex stimulation for pain control induces changes in the endogenous opioid system. Neurology 69:827–834
Manchikanti L, Singh V, Datta S, Cohen SP, Hirsch JA (2009) Comprehensive review of epidemiology, scope, and impact of spinal pain. Pain Phys 12:2149–2150
Mendonca ME, Santana MB, Baptista AF, Datta A, Bikson M, Fregni F, Araujo CP (2011) Transcranial DC stimulation in fibromyalgia: optimized cortical target supported by high-resolution computational models. J Pain 5:610–617
Morgan PJ et al (1994) Melatonin receptors: localization, molecular pharmacology and physiological significance. Neurochem Int 24:101–146
Nayef E, Saadéa B, Suhayl J, Jabbur B (2008) Nociceptive behavior in animal models for peripheral neuropathy: spinal and supraspinal mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol 22:47–86
Nekhendzy V, Fender CP, Davies MF, Lemmens HJ, Kim MS, Bouley DM, Maze M (2004) The antinociceptive effect of transcranial electrostimulation with combined direct and alternating current in freely moving rats. Anesth Analg 98:730–737
Neumann S, Doubell TP, Leslie T, Woolf CJ (1996) Inflammatory pain hypersensitivity mediated by phenotypic switch in myelinated primary sensory neurons. Nature 384:360–364
Nitsche MA, Paulus W (2000) Excitability changes induced in the human motor cortex by weak transcranial direct current stimulation. J Physiol 527:633–639
Nitsche MA, Fricke K, Henschke U, Schlitterlau A, Liebetanz D, Lang N, Henning S, Tergau F, Paulus W (2003) Pharmacological modulation of cortical excitability shifts induced by transcranial direct current. J Physiol 553:293–301
Nitsche MA, Jaussi W, Liebetanz D, Lang N, Tergau F, Paulus W (2004) Consolidation of human motor cortical neuroplasticity by d-cyloserine. Neuropsyhopharmacology 29:1573–1578
Nitsche MA, Cohen LG, Wassermann EM, Priori A, Lang N, Antal A, Paulus W, Hummel F, Boggio PS, Fregni F, Pascual-Leone A (2008) Transcranial direct current stimulation: state of the art 2008. Brain Stimul 1:206–223
Ossipov MH, Kovelowski CJ, Nichols ML, Hruby VJ, Porreca F (1995) Characterization of supraspinal antinociceptive actions of opioid delta agonists in the rat. Pain 62:287–293
Ouyang W, Hemmings HC Jr (2005) Depression by isoflurane of the action potential and underlying voltage-gated ion currents in isolated rat neurohypophyseal nerve terminals. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:801–808
Patil KR, Patil CR, Jadhav RB, Mahajan VK, Patil PR, Gaikwad PS (2009) Anti-arthritic activity of bartogenic acid isolated from fruits of Barringtomia racemosa Roxb. (Lecythidaceae). Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. doi:10.1093/ecam/nep148
Philippe L et al (1997) Relations between functional, inflammatory, and degenerative parameters during adjuvant arthritis in rats. Am J Physiol 273:550–556
Rezazadeh SH, Zaringhalam J, Manakeji H, Kebryaeezadeh A (2009) Anti-inflammatory and anti-hyperalgesic activities of Stachy athorecalyx extracts on CFA-induced inflammation. J Med Plant Res 5(187):191
Rosen AC, Ramkumar M, Nguyen T, Hoeft F (2009) Noninvasive transcranial brain stimulation and pain. Curr Pain Headache Rep 13:12–17
Rubinstein M, Mogil JS, Japón M, Chan EC, Allen RG, Low MJ (1996) Absence of opioid stress-induced analgesia in mice lacking beta-endorphin by site-directed mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:3995–4000
Ruscheweyh R, Wilder-Smith O, Drdla R, Liu XG, Sandkühler J et al (2011) Long-term potentiation in spinal nociceptive pathways as a novel target for pain therapy. Mol Pain 7:20
Schuhmann B, Dietrich A, Sel S, Hahn C, Klingenspor M, Lommatzsch M, Gudermann T, Braun A, Renz H, Nockher WA (2005) A role for brain derived neurotrophic factor in B cell development. J Neuroimmunol 163:15–23
Stein C, Millan MJ, Herz (1988) Unilateral inflammation of the hind paw in rats as a model of prolonged noxious stimulation: alterations in behavior and nociceptive thresholds. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2:451–455
Takano Y, Yokawac T, Masudac A, Niimic J, Tanakad S, Hironakaa N (2011) A rat model for measuring the effectiveness of transcranial direct current stimulation using fMRI. Neurosci Lett 491:40–43
Tal M, Bennett GJ (1994) Neuropathic pain sensations are differentially sensitive to dextrorphan. NeuroReport 5:1438–1440
Tsubokawa T, Katayama Y, Yamamoto T, Hirayama T, Koyama S (1993) Chronic motor cortex stimulation in patients with thalamic pain. J Neurosurg 78:393–401
Volz M, Volz T, Brunoni A, Oliveira J, Fregni F (2012) Analgesic effects of noninvasive brain stimulation in rodent animal models: a systematic review of translational findings. Neuromodulation (in press)
Wachter D, Wrede A, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Taghizadeh-Waghefi A, Nitsche MA, Kutschenko A, Rohde V, Liebetanz D (2011) Transcranial direct current stimulation induces polarity-specific changes of cortical blood perfusion in the rat. Exp Neurol 227:322–327
Wang HY, Crupi D, Liu J, Stucky A, Cruciata G, Di Rocco A, Friedman E, Quartarone A, Ghilardil MF (2011) Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation enhances BDNF–TrkB signaling in both brain and lymphocyte. J Neurosci 31(30):11044–11054
Wegert S, Ossipov MH, Nichols ML, Bian D, Vanderah TW, Malan TP Jr, Porreca F (1997) Differential activities of intrathecal MK-801 or morphine to alter responses to thermal and mechanical stimuli in normal or nerve-injured rats. Pain 71:57–64
Woolfe G, Macdonald AD (1944) The evaluation of the analgesic action of pethidine hydrochloride. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 80:300–307
Wu FS et al (2000) Noncompetitive inhibition of the glycine receptor-mediated current by melatonin in cultured neurons. Brain Res 881:208–211
Yirmiya R, Goshen I (2011) Immune modulation of learning, memory, neural plasticity and neurogenesis. Brain Behav Immun 25:181–213
Zaringhalam J et al (2010) Achillea santolina reduces serum interleukin-6 level and hyperalgesia during complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced inflammation in male Wistar rats. J Chin Integr Med 12:1180–1189
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the following Brazilian funding agencies: National Council for Scientific and Technological Development—CNPq (Dr. I.L.S. Torres, Grant no. 307772/2008-0/2008, Dr. W. Caumo); PROPESQ/UFRGS/PIBIC/CNPq : Committee for the Development of Higher Education Personnel—CAPES (J.R. Rozisky, G. Laste, L.S.N. Adachi); and Graduate Research Group (GPPG) of Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre—HCPA (Dr I.L.S. Torres—Grant 100013). We would like to thank the engineering staff of HCPA for developing the tDCS stimulator.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the contents and writing of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laste, G., Caumo, W., Adachi, L.N.S. et al. After-effects of consecutive sessions of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in a rat model of chronic inflammation. Exp Brain Res 221, 75–83 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-012-3149-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-012-3149-x